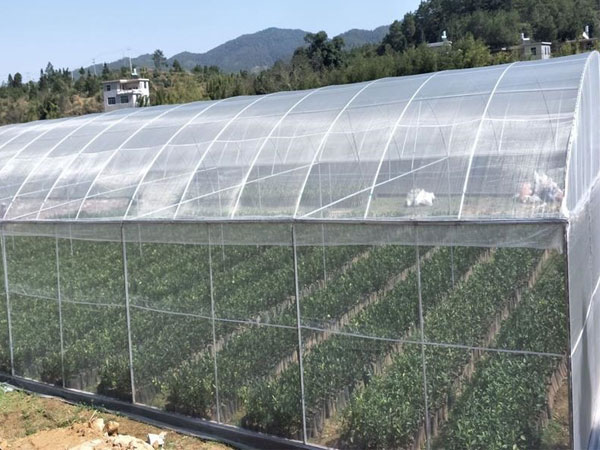
The so-called modern greenhouse builds upon the traditional greenhouse by adding controls for parameters such as temperature, light, and humidity, allowing for the creation of an optimal growth environment for plants and thereby achieving maximum yield. Today, we will introduce the common systems found in a multi-span greenhouse.

The External Shading System of Greenhouses
The primary function of the external shading system is to block excessive sunlight, protecting crops from being scorched by strong light. By preventing a large amount of light from entering, it effectively reduces the accumulation of heat within the greenhouse, offering a better cooling effect compared to the internal shading system. Different shading rates of the curtain can be selected to meet the needs of various crops for sunlight. Additionally, the external shading system also provides protection against hail.
The Internal Shading System of Greenhouses
The shading system opens and closes through gears, racks, or cables. In summer, when the shading curtain is closed during the day, it can effectively reduce the temperature inside the greenhouse. In winter, when the shading curtain is closed at night, it can effectively prevent the internal heat of the greenhouse from escaping through radiation or heat exchange, thereby reducing the operational energy of the greenhouse.
The Interlaced Ventilation System of Greenhouses
The interlaced ventilation system, also known as the push rod ventilation system, is suitable for Venlo-type greenhouses. When ventilating, the gears and racks move under the drive shaft's activation, pushing the push rod forward, and opening the window with the help of the supporting arm. The interlaced ventilation is only suitable for top window systems. Due to differences in gear and rack mechanisms, the interlaced ventilation is divided into two types: track type and crank arm type.
The main difference between the two is that the former has a single rack with a large thrust, suitable for longer greenhouses, while the latter is suitable for shorter greenhouses but has a simpler structure and lower cost. The system comprises gears, racks, push rods, geared motors, drive shafts, supporting arms, and other accessories. The main function of the interlaced ventilation is to utilize natural ventilation to regulate indoor temperature and humidity.
The Fan and Water Curtain Cooling System of Greenhouses
The fan and water curtain cooling system consists of a water curtain, fan, water circulation system, and control devices. It applies the principle of evaporative cooling, with the water curtain and fan installed at both ends of a sealed structure. When the fan operates, it creates negative pressure inside, forcing unsaturated outdoor air to pass through the porous wet surface of the water curtain, causing water to evaporate and thus lowering the indoor temperature.
The Heating System of Greenhouses
The heating system in the greenhouse consists of selecting appropriate heating equipment to meet the heating load requirements of the greenhouse. It generally comprises a heat source, indoor heat dissipation devices, and a heat medium transport system. Related equipment includes boilers, transport pipes, circulating water, radiators, and various control and adjustment valves.

 English
English